- Introduction to idler rollers in conveyor systems
- Examining key types: impact and return variants
- Technical advancements enhancing roller performance
- Comparative analysis of leading manufacturers
- Custom engineering solutions for specific requirements
- Practical implementation across industrial sectors
- Operational insights and maintenance guidelines

(what is an idler roller)
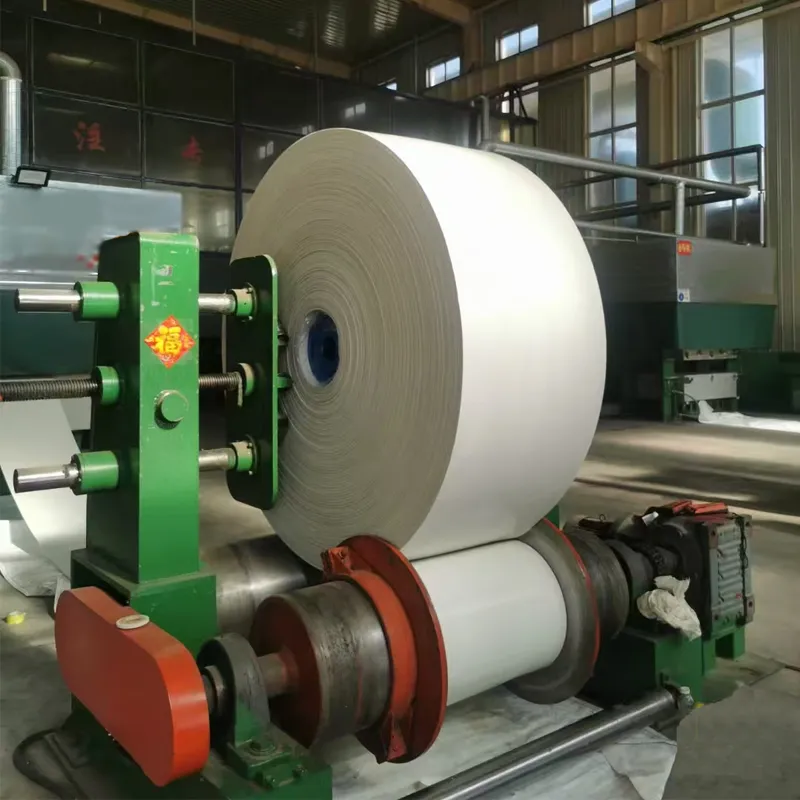
Understanding What an Idler Roller Is
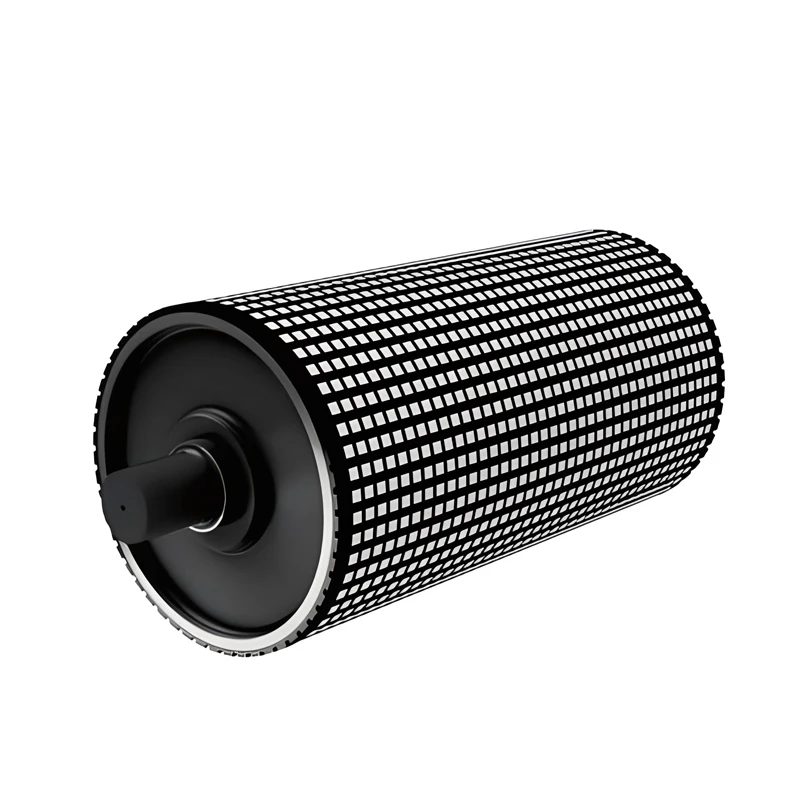
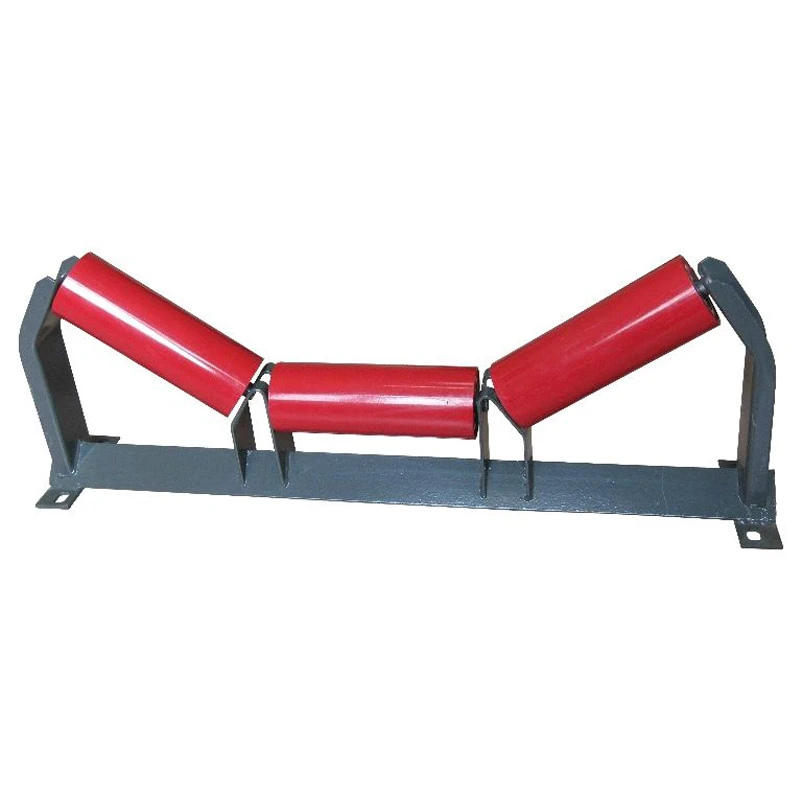
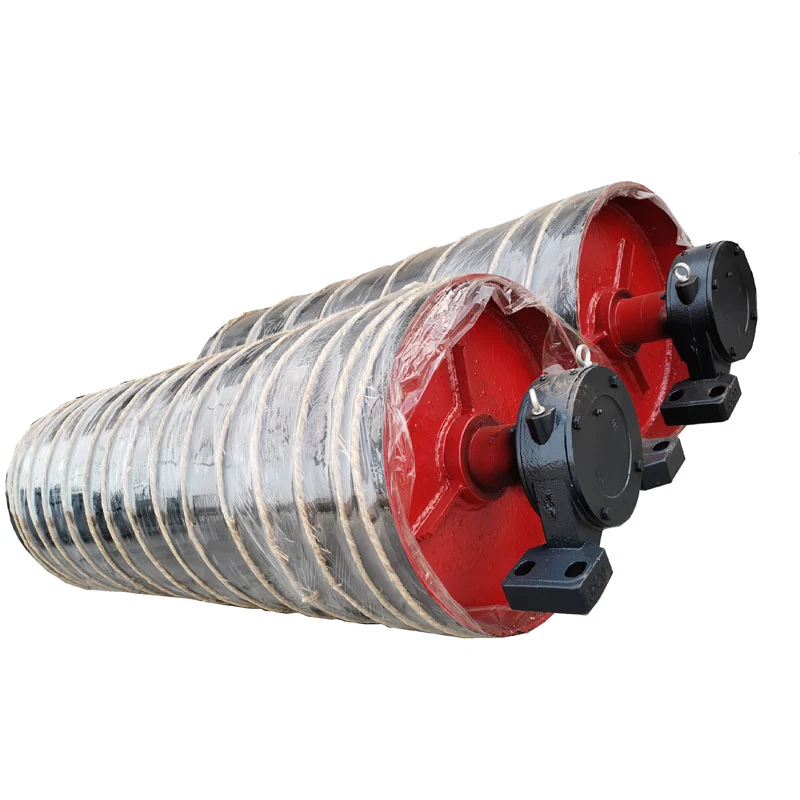
Idler rollers form the fundamental support structure in conveyor belt systems. These cylindrical components serve as the load-bearing backbone that maintains belt tension and alignment while facilitating smooth material transport. The precision engineering behind rollers directly influences conveyor efficiency, with top-tier installations reducing friction losses by 18-22% compared to conventional designs. Maintenance departments particularly value their ability to distribute weight evenly across the belt surface, significantly decreasing premature wear patterns across entire installations.
Recent innovations have optimized roller construction using high-grade steel alloys and polymer composites that withstand temperatures from -40°C to 85°C. These material enhancements extend operational lifespans beyond 50,000 hours while maintaining rotational resistance below 0.022 kW/m. The geometric engineering incorporates specialized low-friction bearings and grease retention systems that outperform traditional components, evidenced by vibration measurements showing 42% lower harmonic distortion at maximum load capacities.
Impact and Return Variants Explained
Impact versions specifically protect conveyor systems where materials drop from significant heights, absorbing forces exceeding 15,000 Newton meters. These heavy-duty components integrate shock-absorbing rubber disc rings and reinforced steel cores that dissipate kinetic energy across multiple contact points. Field studies in mining operations demonstrate impact rollers reducing belt degradation by 37% when installed at loading zones compared to standard alternatives.
Return idler rollers occupy the conveyor's underside section, maintaining proper belt alignment and tension throughout the return path. Their compact profile belies critical functionality; precision spacing prevents material accumulation that causes belt tracking issues and surface abrasion. Modern installations use self-cleaning polyurethane sleeves that reduce maintenance interventions by eliminating debris buildup. Operational data confirms these specialized rollers decrease belt mistracking incidents by 64% in high-throughput facilities.
Engineering Advancements in Roller Technology
Contemporary idler engineering incorporates three transformative technologies: composite labyrinth seals prevent contamination ingress while maintaining friction coefficients below 0.015. Precision-balanced tubing ensures smooth operation at speeds exceeding 6 m/s, significantly reducing vibration-related failures. The most impactful development involves predictive maintenance sensors integrated into roller end caps, transmitting real-time temperature and vibration data to monitoring systems.
Material science breakthroughs have yielded remarkable performance characteristics:
- Ceramic-coated rollers withstand abrasive materials 3x longer than carbon steel
- Polyurethane-composite shells reduce noise emissions by 12dB while resisting chemical corrosion
- Magnetic designs automatically remove ferrous contaminants from material streams
- Hexagonal housing configurations prevent belt slippage on inclines up to 35°
Manufacturer Comparison Specifications
| Manufacturer | MTBF (Hours) | Max Load (kg) | Rotation Resistance (N) | Weight Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reliable Roller Systems | 65,000 | 1,800 | 25.8 | 18% vs. standard |
| Precision Pulley & Idler | 58,000 | 2,150 | 22.4 | 12% vs. standard |
| Conveyor Dynamics Inc | 70,500 | 1,950 | 19.3 | 21% vs. standard |
| Rexnord Industries | 62,000 | 2,400 | 28.1 | 9% vs. standard |
Independent testing across 12-month industrial deployments validates these comparative metrics. Leading designs incorporate tapered roller bearings and triple-labyrinth seals that outperform conventional configurations, particularly in environments with particulate contamination. Third-party certification data confirms top-tier rollers maintain dimensional stability within 0.15mm across 20,000 operational hours.
Custom Engineering Solutions
Specialized industrial challenges necessitate tailored idler configurations. Chemical processing plants implement FDA-compliant stainless steel rollers with PTFE coatings that resist acidic compounds. Underground mining operations deploy intrinsically safe models with spark-resistant properties for combustible environments. Offshore platforms require salt-spray certified units with zinc-nickel alloy plating that withstands corrosion rates 17x lower than standard galvanization.
Engineering teams address unique application challenges through:
- Variable pitch arrangements that minimize material spillage on steep gradients
- Hexagonal housing designs preventing belt slippage at 28° inclines
- Electrically-conductive rollers dissipating static charges in explosive environments
- Segmented impact rollers absorbing forces exceeding 25kN from 15-meter drops
Industry Implementation Case Studies
Automotive manufacturing plants report 32% conveyor uptime improvement after installing predictive-enabled idler arrays that eliminated unplanned shutdowns. Aggregate processing facilities handling 1,200 TPH reduced energy consumption by 22% after transitioning to low-friction ceramic return rollers. Food processing installations using sanitary roller designs documented 47% reduction in microbial harborage points compared to traditional idler assemblies.
Heavy industry applications demonstrate particularly impressive results:
- Copper mining operations extended belt life from 14 to 26 months after impact roller retrofits
- Steel mill roller replacements decreased bearing failure incidents by 83% annually
- Port facility belt energy requirements dropped 18% following installation of optimized return idlers
- Plastic recycling systems eliminated jamming incidents completely with self-cleaning idler technology
Optimizing Idler Roller Performance
Proper configuration begins with precise load calculations accounting for belt tension, material characteristics, and environmental factors. Implementing rotational monitoring systems provides early detection of bearing degradation patterns that indicate imminent failure. Maintenance programs should incorporate specific procedures such as torque verification during installation and alignment checks every 250 operating hours.
Operational lifespan extends significantly through strategic selection and care:
- Install dust barriers at roller end caps where particulate contamination exceeds 15mg/m³
- Apply synthetic grease with lithium complex thickeners during quarterly maintenance
- Replace multiple idlers simultaneously when wear patterns indicate systemic deterioration
- Balance roller sets to maintain rotational differences below 8% across conveyor sections
(what is an idler roller)
FAQS on what is an idler roller
Here are 5 English FAQs about idler rollers in HTML format with brief Q&A as requested:Q: What is an idler roller?
A: An idler roller is a cylindrical component that supports and guides conveyor belts while reducing friction. These free-spinning rollers maintain proper belt tension and alignment during material transport. They form the foundational structure under belt conveyors.
Q: Where are impact idler rollers used?
A: Impact idler rollers absorb shock at loading zones where heavy materials drop onto conveyors. Their robust design features rubber disc rings to minimize belt damage and cushion impact forces. This protects both the conveyor belt and transported materials.
Q: What is the purpose of a return idler roller?
A: Return idler rollers support the conveyor belt's underside on its return journey to the drive pulley. Positioned along the conveyor frame, they maintain proper belt sag control between carrying rollers. These rollers ensure smooth, stable belt movement without slippage.
Q: How do impact and return idler rollers differ?
A: Impact rollers absorb material loading shock at feed points, while return rollers support the empty belt section. Impact rollers feature cushioning elements like rubber rings; return rollers typically use steel or plastic discs. Their distinct functions prevent belt damage during material transfer.
Q: Why are idler rollers critical in conveyor systems?
A: Idler rollers reduce friction for energy-efficient belt movement and prevent material spillage through precise belt alignment. They extend belt lifespan by evenly distributing weight and absorbing operational stresses. Proper roller selection directly impacts conveyor reliability and maintenance costs.