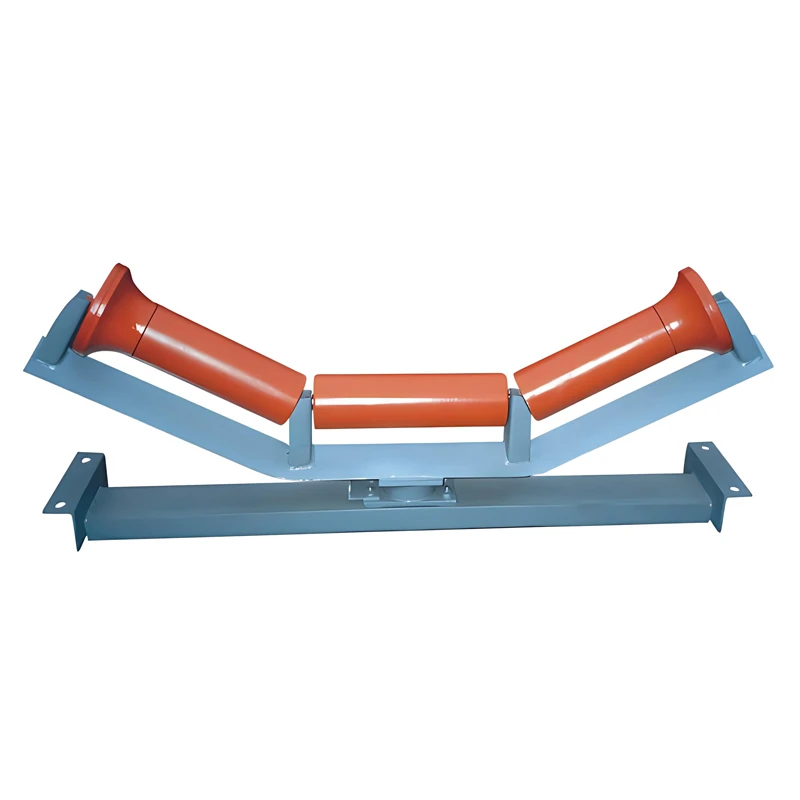
- Critical Technical Specifications and Advantages
- Comprehensive Manufacturer Comparison Analysis
- Custom Engineering Solutions for Unique Requirements
- Industry-Specific Applications and Case Studies
- Performance Benchmarking Data Analysis
- Maintenance Protocols for Extended Service Life
- Future Material and Design Innovations

(conveyor belt roller types)
Understanding Conveyor Belt Roller Types for Material Handling
Conveyor systems represent the vascular network of industrial operations, where roller selection directly impacts throughput capacity and operational expenditure. Industry reports indicate roller failures cause 23% of unexpected conveyor downtime, highlighting the critical importance of proper roller selection. These cylindrical components appear deceptively simple but incorporate sophisticated engineering principles. Selection parameters must include load ratings, rotational resistance values, environmental conditions, and material compatibility factors that govern performance longevity.
Technical Specifications and Design Advantages
Roller construction determines performance capabilities under industrial stress conditions. Steel rollers provide maximum load capacity up to 2,500kg per roller with minimal deflection (under 0.3mm), making them ideal for heavy mining applications. For corrosive environments, 316L stainless steel rollers demonstrate salt spray resistance exceeding 1,000 hours without degradation. Impact rollers with rubber disc configurations reduce vibration transmission by 70% compared to rigid designs, critical for protecting fragile goods during transfer points. Innovative polymer rollers achieve 40% weight reduction while maintaining 1,100kg load ratings, significantly decreasing energy consumption per meter conveyed.
Top Manufacturer Comparison Analysis
| Manufacturer | Service Life (Hours) | Max Load (kg) | Rotational Resistance (N) | Specialization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rexnord | 30,000+ | 2,500 | 2.3–3.1 | Heavy-Duty Mining |
| Interroll | 25,000 | 1,800 | 1.8–2.5 | Warehouse Automation |
| Rulmeca | 28,000 | 2,200 | 2.1–3.0 | Bulk Handling |
| LBS Rollers | 22,000 | 1,500 | 1.5–2.2 | Food-Grade Systems |
Independent testing by Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association reveals significant performance differences between standard rollers and premium alternatives. Higher-grade bearings increase service intervals by 300%, while specialized sealing systems prevent 87% of contamination-related failures. Mining operations using reinforced rollers report 17% lower maintenance costs despite 35% higher initial investment, demonstrating superior lifecycle economics.
Industry-Specific Engineering Solutions
Custom roller configurations address unique operational challenges across sectors. In aggregate processing, impact cradle rollers withstand forces exceeding 50kJ while maintaining alignment precision within 0.5 degrees. Food processing facilities implement antimicrobial nylon rollers that withstand daily high-pressure washdowns at 80°C without degradation. Warehouse automation systems increasingly adopt motorized rollers with integrated controllers, reducing energy consumption by 60% compared to traditional drive systems. Recent advances include RFID-embedded rollers that transmit real-time temperature and vibration data, enabling predictive maintenance protocols.
Operational Case Studies and Metrics
Automotive manufacturing plants implementing tapered rollers reported 92% reduction in conveyor belt tracking issues, decreasing maintenance labor requirements by 45 hours weekly. A cross-border parcel facility reduced energy expenditure by $120,000 annually after transitioning to low-friction polymer rollers throughout their 8km sorting system. In extreme temperature steel mills, ceramic-coated rollers maintained performance at 600°C where conventional rollers failed within weeks, extending replacement cycles from monthly to quarterly intervals.
Proactive Maintenance Methodologies
Proper lubrication protocols can extend roller service life by 200% according to bearing manufacturers. Utilizing infrared thermography identifies temperature anomalies indicating developing friction issues. Implementing rotational resistance testing identifies rollers exceeding 4.0N resistance before visible deterioration occurs. Facilities adopting quarterly alignment verification experience 68% fewer catastrophic roller failures. Warehouse managers report 30% maintenance reduction through implementing tapered roller configurations that automatically maintain proper belt tracking.
Optimizing Operations Through Conveyor Roller Types
The evolution of conveyor belt roller types
continues with nanomaterials entering commercial production, offering potential 70% weight reduction without structural compromise. Electromagnetic roller technologies being prototyped eliminate physical bearings entirely, targeting maintenance-free operation exceeding 100,000 hours. Advanced composites withstand extreme chemical environments previously requiring frequent ceramic replacements. As Industry 4.0 progresses, roller-integrated sensors will become standard, providing real-time health monitoring data directly to facility management systems.

(conveyor belt roller types)
FAQS on conveyor belt roller types
Here are 5 FAQ pairs about conveyor belt roller types in HTML format:Q: What are the main types of conveyor belt rollers?
A: Key roller types include carrying rollers (supporting the load), impact rollers (for loading zones), return rollers (beneath the conveyor), and guide rollers (for belt tracking). Each serves a specific function in material handling systems with distinct designs.
Q: How do belt conveyor roller types impact system performance?
A: Roller selection directly affects efficiency, noise levels, and maintenance needs. Properly specified rollers reduce energy consumption by minimizing friction while incorrect types cause premature belt wear and material spillage, increasing downtime.
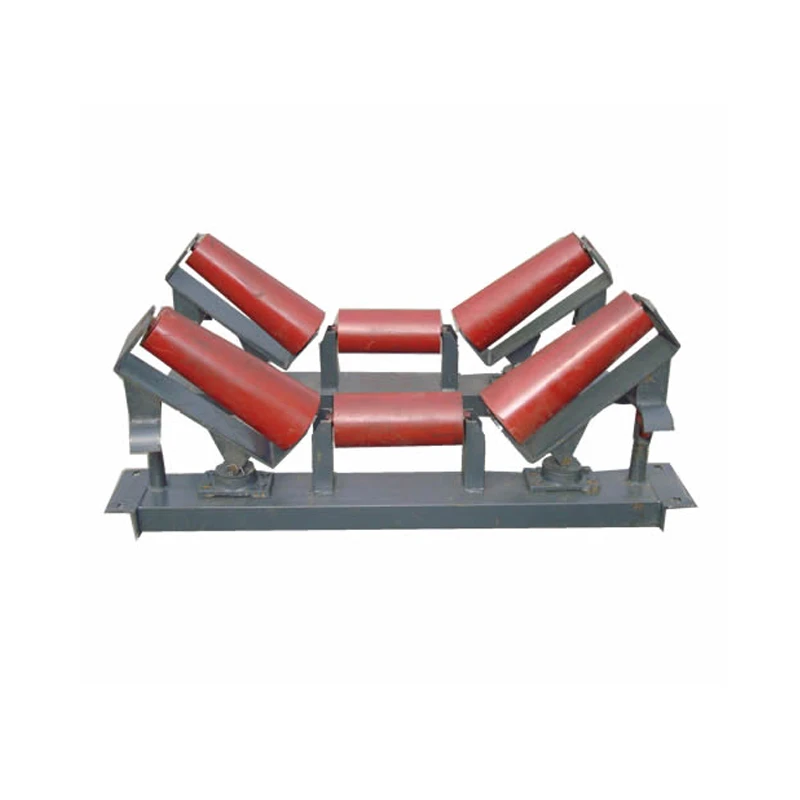
Q: What distinguishes troughing rollers from other conveyor roller types?
A: Troughing rollers feature multi-roll arrangements (usually 20-45° angles) that curve the belt into a U-shape. This design prevents material spillage and increases carrying capacity compared to flat rollers, making them ideal for bulk handling.
Q: When should impact rollers be used in conveyor systems?
A: Impact rollers are essential at loading points where heavy or sharp materials drop onto the belt. Their spring-mounted design and rubber rings absorb shock, protecting both the belt and roller bearings from impact damage.
Q: Which conveyor roller types require minimal maintenance?
A: Sealed bearing rollers with precision-grade steel shells require least maintenance. Features like labyrinth seals prevent contaminant ingress, while specialized coatings reduce material buildup - both extending service intervals to over 30,000 hours in standard conditions.