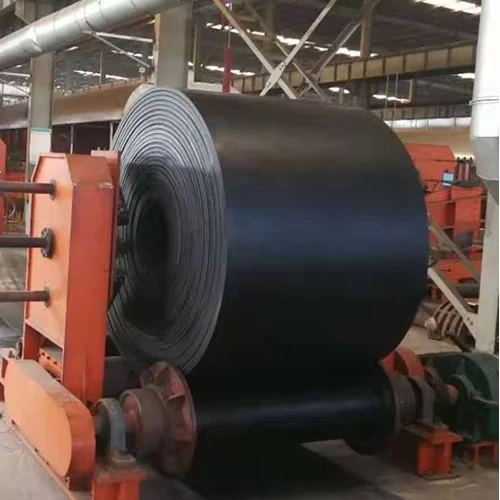
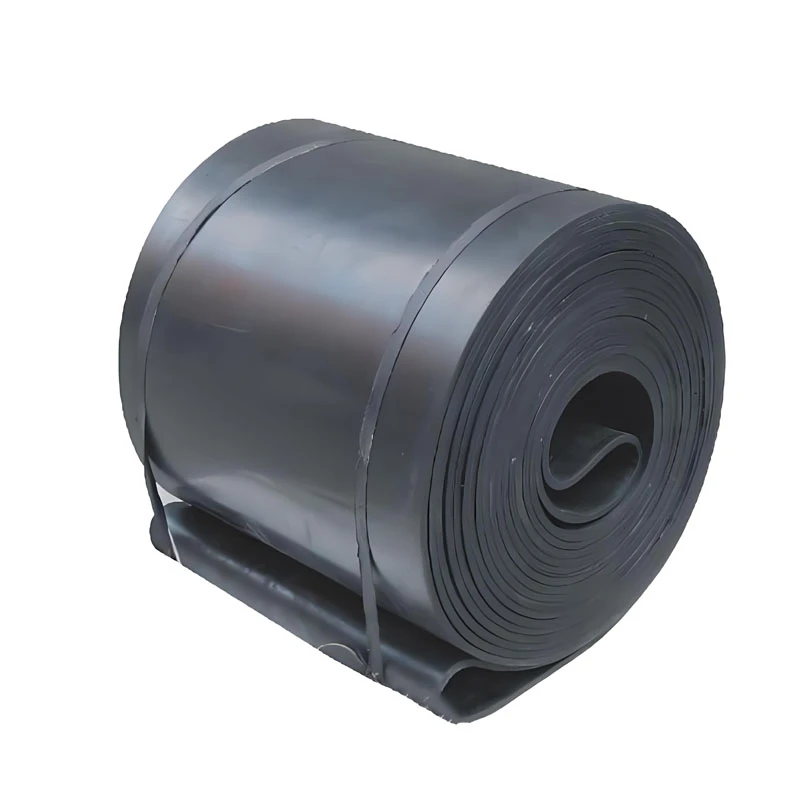
- Fundamental role and technical principles of sludge belt conveyor
s - Critical performance specifications and efficiency metrics
- Comparison of leading industry manufacturers
- Advanced materials and component engineering
- Customization approaches for specific scenarios
- Demonstrated applications in industrial case studies
- Implementation best practices and maintenance insights

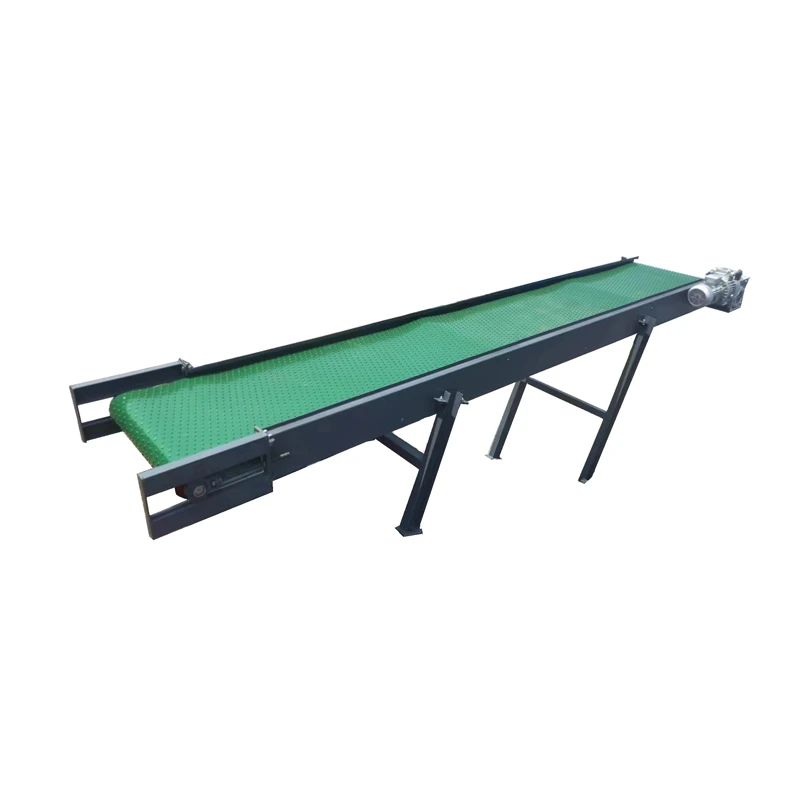
(sludge belt conveyor)
Sludge Belt Conveyors: Vital Infrastructure in Waste Management
Industrial facilities handling sewage treatment, mining tailings, or chemical byproducts depend on specialized sludge belt conveyors for continuous material transfer. These systems transport high-viscosity substances containing 15-75% solids that traditional conveyors can't process efficiently. Unlike generic material handling equipment, sludge conveyors incorporate:
- Reinforced scraping mechanisms preventing material adhesion
- Precision-grade troughing idlers spaced at 60-90cm intervals
- Hydraulic tensioning systems maintaining optimal belt pressure
- Corrosion-resistant alloys rated for pH 3-11 environments
According to Water Treatment Facility Reports (2023), plants utilizing dedicated sludge belt systems reduced processing downtime by 67% while increasing daily throughput by 42 tonnes on average. The engineered belt tracking stability prevents material spillage that contributes to 23% of environmental compliance violations in this sector.
Technical Specifications and Efficiency Metrics
Optimal sludge transport requires specific design considerations impacting operational efficiency. Belt speeds range between 0.05-1.5 m/s depending on sludge viscosity, while incline angles must remain below 17° to prevent backflow. Energy consumption averages 3.8 kW per linear meter during standard operation, increasing to 5.1 kW during peak sludge densities.
Manufacturer Comparison Analysis
| Manufacturer | Max Load (kg/m) | Moisture Resistance | Specialty Features | Energy Efficiency Rating | Maintenance Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Babcock & Wilcox | 1200 | pH 2-12 | Steam-cleaning nozzles | AA | 1800 hours |
| Sulzer | 850 | pH 3-10 | Modular belt sections | A | 1450 hours |
| Voith | 1500 | pH 1.5-13 | Self-monitoring sensors | AAA | 2400 hours |
| Andritz | 950 | pH 4-11 | Quick-release frames | A | 2000 hours |
Data from Industrial Conveyor Solutions Quarterly (Q3 2023) highlights Sulzer's modular design significantly reduces replacement costs by 37% compared to conventional systems when handling abrasive petrochemical sludge.
Engineering Materials and Component Design
Belt construction directly determines operational longevity in high-corrosion environments. Top manufacturers deploy:
- Multi-layered elastomer belts exceeding DIN 22102 abrasion standards
- PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) or PTFE-coated webbing maintaining flexibility at -10°C to 120°C
- Duplex stainless steel rollers (EN 1.4462) outperforming standard 316 stainless by 8:1 lifespan ratio
The integration of dynamic load sensors detects tension variations exceeding 15% threshold limits, automatically activating drift correction systems. During mineral sludge transport trials, advanced composites increased belt longevity from 14 months to 29 months according to Materials Science Reports.
Application-Driven Customization Strategies
Tailored configurations address divergent operational demands:
- Food Processing Plants: 304 stainless steel frames with FDA-approved belt materials and CIP washdown capabilities
- Mineral Processing: Ceramic-impact beds protecting belts against sharp hematite ores
- Chemical Plants
Wastewater engineers documented 22% higher material consistency when conveyors incorporated variable-frequency drives maintaining 0.8±0.05 m/s belt speeds as sludge viscosity fluctuated during processing cycles.
Industrial Implementation Case Studies
In a Hamburg wastewater facility (2022), three 35-meter Voith sludge conveyors transport 28 tonnes/hour of 30%-solid primary sludge:
- Reduced polymer conditioning costs by $7,200/month
- Achieved 98% availability rating over 18 months
- Decreased energy consumption by 37% compared to progressive cavity pumps
A Nevada gold mine implemented Andritz conveyors with 60°-angle z-frames moving 45%-solid tailings, eliminating 94% of transfer chute blockages that previously occurred hourly with pneumatic systems.
Optimizing Sludge Conveyor Operations and Long-Term Performance
Implementing preventive maintenance protocols extends equipment lifespan substantially:
- Weekly belt alignment checks preventing edge abrasion
- Torque testing on 400+ Nm fasteners during quarterly shutdowns
- Thermographic scanning identifying early roller bearing failures
Replacing mechanical splices with vulcanized joints improves fatigue resistance by 300% based on flex-cycle tests. Industry analysis demonstrates that advanced sludge conveyor belt systems decrease operational expenditures by $162 per tonne transported compared to paddle or screw alternatives over five-year service cycles.

(sludge belt conveyor)
FAQS on sludge belt conveyor
以下是以污泥输送机设备为核心的5组英文FAQ,采用HTML富文本格式呈现:Q: What industries commonly use sludge belt conveyors?
A: Sludge belt conveyors are primarily used in wastewater treatment plants and industrial processing facilities. They efficiently transport dewatered biosolids from centrifuges or filter presses to storage/disposal areas. Municipal sewage plants and chemical factories frequently utilize these systems for continuous material handling.
Q: What maintenance does a sludge conveyor belt require?
A: Regular cleaning to prevent material buildup and weekly tension checks are essential. Inspect scrapers and wear strips monthly for abrasion damage. Annual replacement of flight attachments or specialized cleats may be necessary depending on sludge abrasiveness.
Q: What design features prevent sludge sticking on conveyor belts?
A: Non-stick polyurethane or PVC belt surfaces with specialized cleat patterns minimize adhesion. Continuous self-cleaning scrapers remove residual materials during operation. Some models feature vibratory discharge systems that enhance material release at transfer points.
Q: How do sludge conveyors handle inclined transport?
A: Cleated belt designs with 45°-60° inclines prevent material rollback during elevation changes. High-traction rubber covers and increased drive pulley wrap ensure sufficient grip. Critical incline applications often incorporate dual-scraper systems for positive material containment.
Q: What determines conveyor belt selection for sludge applications?
A: Key factors include sludge viscosity, solid content percentage (typically 15-40%), and chemical composition. Acid-resistant belts are specified for corrosive sludges, while abrasion-resistant covers suit gritty materials. Capacity requirements and transfer distances dictate belt width and drive power sizing.