Key sections covered in this technical review:
- Performance impact metrics and operational benefits
- Critical engineering advantages over conventional systems
- Manufacturer capability assessment matrix
- Belt profile customization parameters
- Industry-specific application engineering
- Maintenance impact on lifecycle costs
- Future material handling solutions development

(sidewall conveyor belt)
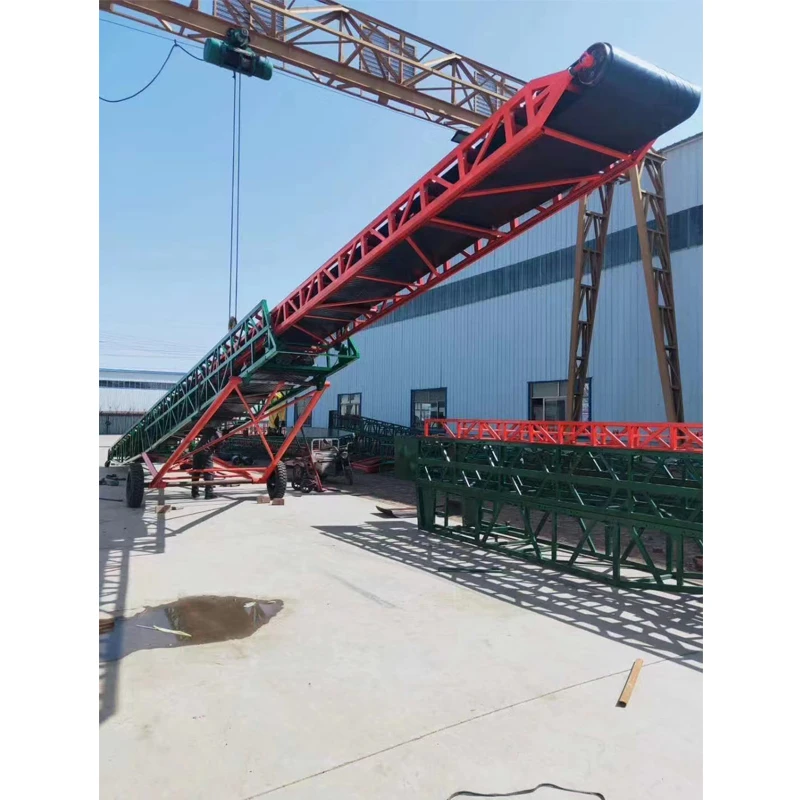
Understanding Sidewall Conveyor Belt Fundamentals
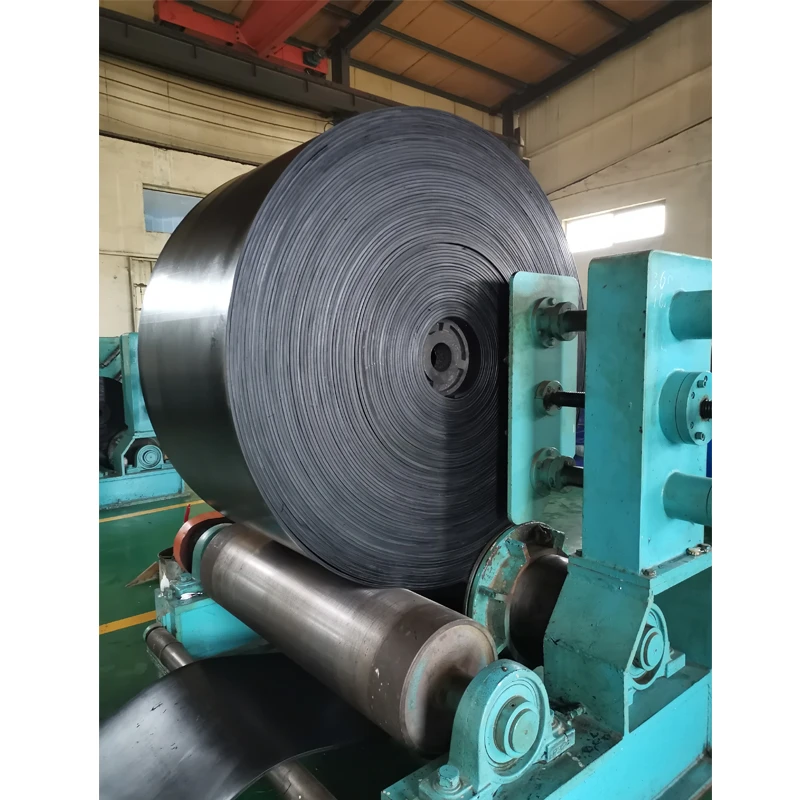
Steep angle material transport systems require specialized engineering solutions beyond conventional flat belts. The corrugated sidewall conveyor belt
represents a transformative technology in bulk handling applications where space constraints or process requirements demand elevated inclinations. These integrated systems combine flexible side barriers with cleated surfaces to securely transport materials at angles exceeding 45° - eliminating transfer points while maintaining material integrity.
Operational Efficiency Metrics
Facilities upgrading to corrugated sidewall systems document measurable performance improvements. Bulk terminal operators report up to 60% footprint reduction versus multi-stage transfer configurations. Cement plants demonstrate capacity increases of 40-50% at equivalent power draw due to eliminated transfer points. Mining operations achieve spillage reduction exceeding 98% compared to conventional systems during vertical conveyance. Power consumption analyses show consistent energy savings between 15-28% for equivalent tonnage over skip hoist alternatives.
Structural Engineering Advantages
Modern corrugated designs incorporate multiple reinforcement layers within a single continuous belt structure. Transverse cleats are integrally molded with the base belt at precise intervals (typically 50-2000mm) and heights (15-630mm) based on application requirements. High-grade rubber compounds with tear resistance ratings exceeding 30N/mm withstand impact loading from oversized materials. Specialized corrugation patterns prevent material backflow during intermittent operation while providing lateral stability at maximum loading. Radial flexibility allows navigation around pulleys as small as 300mm diameter without structural compromise.
Manufacturer Capability Assessment
| Manufacturer | Max Width (mm) | Incline Capability | Specialized Compounds | Sidewall/ Cleat Options | Testing Facilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ContiTech | 2400 | 90° | Oil/Fire/Heat/Abrasion | 9 profiles | Full-scale incline test rig |
| Flexco | 2000 | 45°-60° | Abrasion/Chemical | 5 profiles | Material adhesion lab |
| Bando | 2200 | 70° | Food-grade/High Temp | 7 profiles | Dynamic load simulation |
| Habasit | 1800 | 40°-55° | Static-dissipative | 4 profiles | Wear resistance testing |
Customization Solutions
Application-specific engineering requires careful parameter matching:
- Cleat Geometry: Chevron, T-shaped, or inverse configurations determined by material flow characteristics and cleaning requirements
- Reinforcement Materials: EP fabric plies (2-8 layers) or steel cord reinforcement for tensile strength ranging from 200-5000N/mm
- Compound Selection: Abrasion-resistant covers (10-12mm thickness) with tear resistance ratings 150% greater than standard materials
- Modular Options: Interlocking segments for simplified maintenance in corrosive environments with vulcanized splice integrity
Industry Implementation Case Studies
Mineral Processing Application: Copper concentrator plant implemented 28° incline system replacing three transfer points with custom 2000mm width belt featuring 400mm corrugated barriers and tungsten-reinforced cleats. Resulted in 32% reduction in dust emissions and 41% decrease in component failures annually. Agricultural Application: Grain terminal utilizes 35° enclosed sidewall belt conveyor design with FDA-compliant compounds and specialized cleaning blades. Achieved 99.8% material containment while eliminating explosion hazards through static control. Recycling Application: Municipal waste facility installed 60° incline corrugated system with penetration-resistant top cover and steel cleat reinforcement. Reduced downtime by 67% while handling 25% increased throughput volume.
Advanced Sidewall Belt Conveyor Design
Current engineering advances focus on energy optimization through predictive modeling of material flow dynamics during vertical conveyance. Finite element analysis enables precise wall thickness reduction while maintaining structural integrity - achieving up to 18% weight reduction without performance compromise. Ceramic-embedded wear zones now extend service life beyond 100,000 operational hours in high-abrasion applications. Smart belt technology integrates embedded sensors monitoring wear patterns and splice tension for predictive maintenance scheduling. These innovations establish modern sidewall conveyor belts as the definitive solution for vertical material handling challenges across multiple industries with measurable operational advantages.

(sidewall conveyor belt)
FAQS on sidewall conveyor belt
Q: What is a sidewall conveyor belt?
A: A sidewall conveyor belt features vertical sidewalls bonded to a flat base belt, enabling steep-angle material transport. These belts prevent spillage of bulk materials like grains or aggregates during inclined conveyance. They eliminate the need for transfer points in multi-directional systems.
Q: How does a corrugated sidewall conveyor belt improve efficiency?
A: The corrugated design creates deeper troughs that contain materials securely at 30°-90° inclines. Its overlapping sidewall pockets minimize gaps between belts and cleats during curves, reducing material loss. This reduces spillage by up to 98% compared to flat belts.
Q: What factors determine sidewall belt conveyor design?
A: Key design considerations include material characteristics, required incline angle, and sidewall height/cleat type. Engineers calculate belt tension, pulley diameter, and drive power based on transport volume and vertical lift. Corrugated sidewall profiles must match roller transitions to prevent folding.
Q: Where are corrugated sidewall belts typically used?
A: These belts excel in steep incline applications like cement plants, power stations, and mining operations. They handle free-flowing bulk materials including coal, fertilizers, and wood chips. Common installations include ship loaders and elevated transfer points where space is limited.
Q: How do cleats enhance sidewall conveyor belt performance?
A: Cleats perpendicular to the belt create pockets that retain material during inclines. They synchronize with corrugated sidewalls to maximize volume capacity. Their spacing and height are customized to prevent backslide based on material angle of repose.