- The Essential Role of Manual Belt Conveyors in Industry
- Core Components and Functionality Breakdown
- Technical Advantages Driving Modern Operations
- Comparative Analysis of Leading Manufacturers
- Customization Strategies for Specific Applications
- Real-World Implementation Scenarios
- Maintenance Protocols and Resource Availability
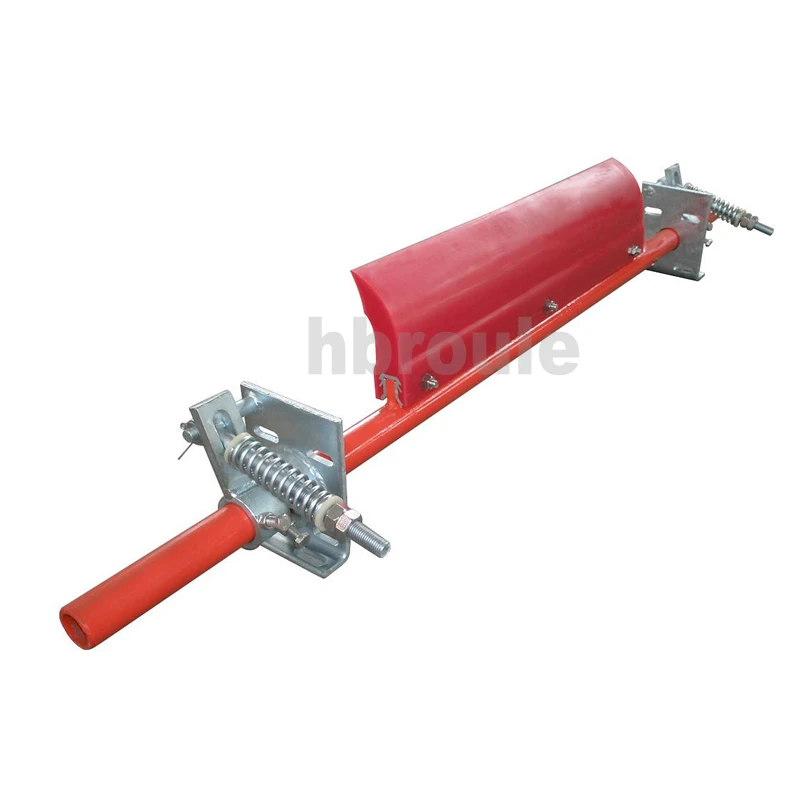

(manual belt conveyor)
Understanding the Critical Functions of Manual Belt Conveyors
Manual belt conveyors serve as the backbone for numerous material handling operations where simplicity and direct control are paramount. Unlike automated systems, these conveyors allow operators to make real-time adjustments based on immediate production needs. Industries from agricultural processing to parcel distribution rely on their flexibility—a single installation typically handles 200% more product variations than rigid automated alternatives.
Key operational advantages stem from their mechanical straightforwardness. Operators can visually monitor product flow without complex sensors, while the physical belt interface enables quick intervention if jams occur. Most installations recoup their investment within 14-18 months, compared to 3+ years for fully automated equivalents. Typical belt widths range from 300mm for small-parts assembly to 1500mm for bulk material handling, with standard loading capacities between 15kg/m and 500kg/m depending on belt composition and roller spacing.
Engineering Fundamentals and Structural Configuration
The architecture of manual belt conveyor
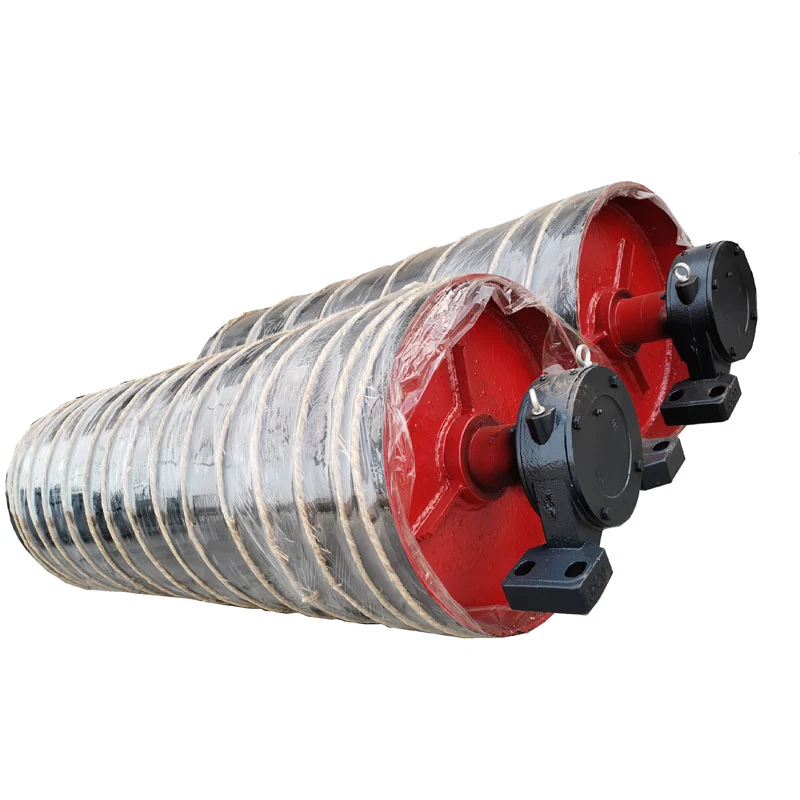
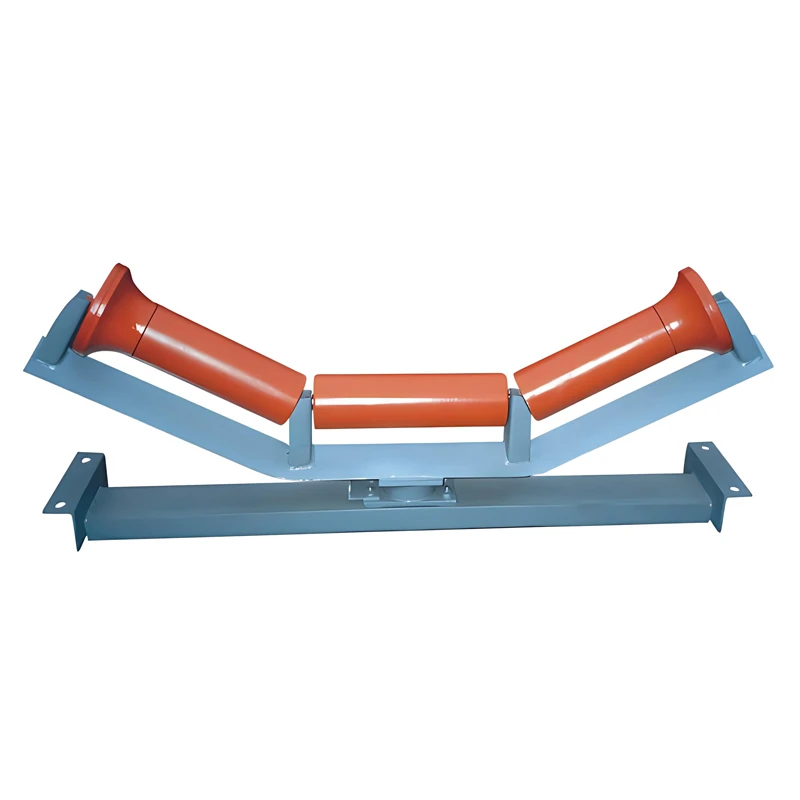
s comprises three critical subsystems: power transmission, support framework, and containment structures. Drive assemblies feature direct-chain or shaft-mounted reducers with 0.37kW to 7.5kW motors. The belt support system utilizes either steel rollers (standard 89mm or 114mm diameter) with 150mm-300mm spacing or solid slider beds for lighter applications.
Tensioning mechanisms employ gravity take-ups (70% of installations) or screw adjusters, maintaining optimal 0.5-3% belt tension. Critical specifications determining longevity include impact idler configurations at loading zones and belt scrapers reducing material carryback by 82-95%. Proper alignment ensures belt tracking stays within 2% of centerline, significantly extending belt service life beyond the typical 30,000-60,000 operational hours.
Performance Enhancements and Modern Technological Integration
Contemporary manual belt conveyor designs incorporate enhancements that boost efficiency while preserving operational simplicity. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) now enable 10-100% speed adjustments, decreasing energy consumption by 25-40% during partial-load operations. Self-tracking rollers with tapered profiles reduce maintenance interventions by maintaining alignment within ±5mm even under uneven loading.
Composite belt materials demonstrate significant durability improvements—modern PVC/Nitrile blends last 50% longer than traditional rubber belts in abrasive environments. Polyurethane cleats vulcanized onto the belt surface enhance incline conveyance up to 28° without slippage. Additionally, modular design approaches permit component replacement in under 30 minutes versus 4+ hours for welded-frame alternatives. These innovations maintain the manual operation principle while substantially boosting productivity metrics.
Vendor Comparison and Selection Parameters
| Manufacturer | Price Range | Max Load (kg/m) | Warranty | Maintenance Index | Custom Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intralox Basic Series | $8K-$25K | 380 | 2 years | 4.2 | 12 weeks |
| Dorner 2200 | $6K-$18K | 260 | 3 years | 3.8 | 8 weeks |
| Hytrol TA Medium Duty | $9K-$33K | 520 | 1 year | 4.7 | 16 weeks |
| Siemens ELP Compact | $14K-$40K | 430 | 5 years | 2.9 | 6 weeks |
Lower Maintenance Index indicates easier serviceability (Scale: 1=best, 5=worst)
Selection criteria should balance three key parameters: operational environment severity (assessed via contamination levels and temperature extremes), peak loading requirements (factoring in surge potential), and accessibility for maintenance. Organizations with high product variability typically prioritize conveyor systems offering modular accessories like adjustable side guides and quick-change belt systems. The Siemens ELP series leads in corrosion resistance with stainless steel construction achieving 200% longer service life in washdown environments, while Hytrol systems dominate heavy-industrial applications requiring >500kg/m loading capacity.
Application-Specific Engineering Modifications
Optimizing manual belt conveyors requires precision customization aligned with application requirements. Food processing operations often incorporate FDA-grade white urethane belts with flush-mounted bearings to eliminate contamination traps. For bulk material handling, engineers increase belt trough angles to 45° and implement specialized covers reducing dust emissions by 97%—a critical OSHA compliance factor.
Component-level modifications dramatically impact performance: ceramic-lagged drive pulleys prevent belt slippage in high-moisture environments, while magnetic head pulleys provide inline metal detection. Hot-material handling (up to 200°C) demands specialized belt compounds like Teflon-coated fiberglass, plus expansion joints accommodating ±15mm thermal movement. Such customizations typically add 15-25% to base system costs but yield operational savings exceeding 300% of the premium within three years through reduced downtime and increased throughput.
Industry Implementation Case Evidence
A Midwest automotive parts manufacturer redesigned their manual conveyor system implementing three key modifications: zoned VFD control allowing 40% reduced line speed during partial shifts, replaceable impact bars at loading points, and thermal-bonded belt joints instead of mechanical fasteners. These changes decreased maintenance costs by $16,500 annually while eliminating 97% of belt-related stoppages.
In packaging distribution centers, customized transfers between conveyors reduced product damage from 0.8% to 0.15% by implementing curved transitions with computer-modeled belt trajectories. Another installation handling recycled materials incorporated self-cleaning rollers with reverse spiral patterns, decreasing cleaning labor requirements by 15 person-hours per week while preventing belt damage from trapped debris. These examples demonstrate how targeted improvements yield measurable efficiency gains within manual belt conveyor frameworks.
Essential Maintenance Procedures and Manual Belt Conveyor Documentation
Proactive preservation of manual belt conveyor systems centers on three pillars: periodic inspections, component condition monitoring, and documentation utilization. Daily walkthroughs should verify belt tracking alignment within ±3mm and inspect pulley lagging integrity. Thermal imaging every 500 operating hours identifies motor bearing anomalies 90% earlier than vibration analysis alone, preventing catastrophic failures.
Every belt conveyor manual contains specific maintenance schedules—typically calling for gearbox oil changes at 2,000-hour intervals and belt tension checks every 250 hours. Proper reference to the belt conveyor maintenance manual reduces service errors by 75% according to maintenance logs from 62 facilities. Most manufacturers provide belt conveyor manual PDF files containing exploded-view diagrams with torque specifications for all critical connections. Third-party resource hubs like Conveyor Maintenance Institute offer supplemental materials addressing common issues like edge fraying or roller degradation in contaminated environments. Maintaining these resources ensures operational continuity and extends equipment lifespan beyond the projected lifecycle.
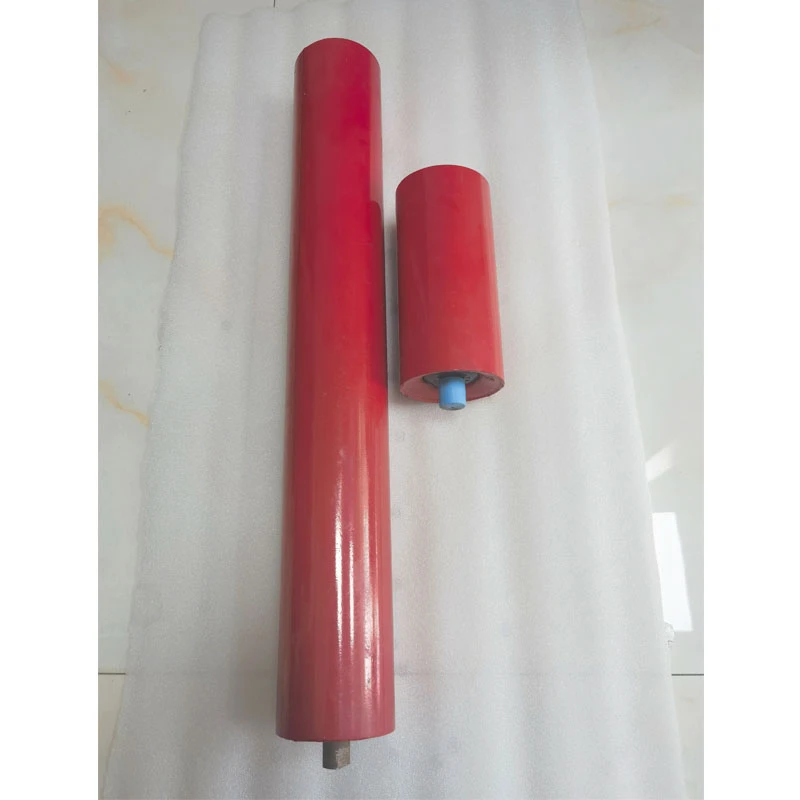

(manual belt conveyor)
FAQS on manual belt conveyor
Q: Where can I find a belt conveyor manual PDF?
A: Most manufacturers provide belt conveyor manual PDFs on their official websites under "Support" or "Resources." Alternatively, contact the supplier directly for an electronic copy. Always verify it matches your conveyor model.
Q: What's included in a belt conveyor maintenance manual?
A: A typical maintenance manual covers lubrication schedules, belt tension adjustments, and component inspection guidelines. It also includes troubleshooting charts and safety protocols. Some manuals provide wear-and-tear lifecycle diagrams.
Q: How to manually operate a belt conveyor?
A: Start by verifying emergency stops are released and guards are secured. Use the manual override switch or hand crank (if equipped) for低速operation. Always follow lockout-tagout procedures outlined in the belt conveyor manual.
Q: Are manual belt conveyors compliant with OSHA standards?
A: Yes, when operated per the manufacturer's manual and OSHA 1926.555 regulations. The belt conveyor maintenance manual should specify required safety features like emergency pull cords and proper guarding installations.
Q: How often should manual belt conveyor inspections occur?
A: Daily visual checks for debris and belt alignment are recommended. Full inspections per the belt conveyor manual (including roller bearings and motors) should occur monthly. Document all findings as per OSHA recordkeeping rules.