The electromagnetic iron remover is a critical component in modern industrial material handling systems, designed to remove ferromagnetic impurities from raw materials. This advanced technology ensures the safe and efficient operation of mechanical equipment such as crushers, grinders, and conveyor systems by preventing damage caused by metallic contaminants. By integrating this device into production lines, industries can significantly improve material quality and reduce maintenance costs.
Product Overview
Manufactured by Hebei Roule Transport Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd., the electromagnetic iron remover is engineered to address the unique challenges of ferromagnetic impurity removal in diverse industrial applications. The device operates through a combination of magnetic field strength and strategic installation, ensuring optimal performance in environments ranging from mining operations to food processing facilities.
The iron remover features a suspended conveyor magnet design that allows for continuous suction and disposal of iron particles. Its adaptability to different unloading methods—manual, automatic, and program-controlled—makes it suitable for both small-scale operations and large industrial complexes.
Key Features and Advantages
The electromagnetic iron remover offers several distinct advantages over traditional methods of impurity removal:
- High Magnetic Field Strength: The device generates a powerful magnetic field that effectively captures even small ferromagnetic particles, ensuring thorough purification of raw materials.
- Adjustable Installation: The iron remover can be positioned at optimal heights to maximize its effectiveness. Lower suspension heights enhance iron removal efficiency, while proper alignment prevents damage to conveyor belts.
- Continuous Operation: Unlike intermittent cleaning methods, the electromagnetic iron remover provides uninterrupted impurity removal, minimizing production downtime.
- Wide Applicability: The device is compatible with various industries, including metallurgy, mining, power generation, and food processing, making it a versatile solution for different material handling needs.

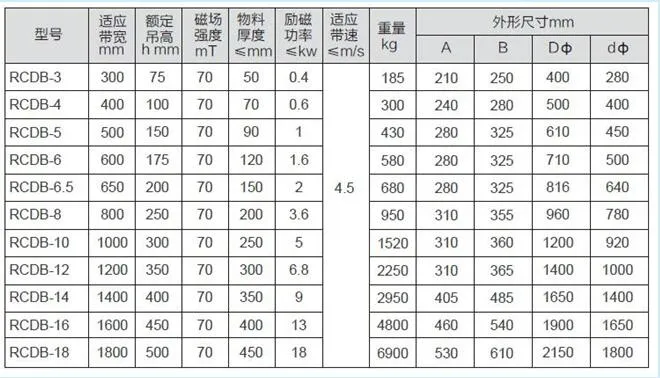
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Field Strength | Up to 1200 Gauss (varies by model) |
| Power Supply | AC 220V/50Hz or DC 24V (customizable) |
| Material Handling Capacity | Up to 500 kg/hour (depending on application) |
| Installation Options | Suspended, fixed, or conveyor-mounted |
| Operating Temperature Range | -20°C to 60°C |
| Protection Rating | IP54 (dust and water resistant) |
Applications in Industrial Processes
The electromagnetic iron remover is widely used across multiple sectors, as highlighted by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) in its research on industrial material handling systems. Key applications include:
- Metal Processing: In steel mills and metal mines, the device prevents large iron parts from damaging crushers and grinders, as noted in NIST's 2023 report on industrial safety standards.
- Cement and Construction Materials: By removing metallic contaminants, the iron remover ensures the quality of raw materials used in cement production and other building material manufacturing processes.
- Food and Feed Industry: The device maintains hygiene standards by eliminating ferromagnetic impurities that could pose health risks to consumers.
- Waste Management: In recycling facilities, the electromagnetic iron remover recovers valuable steel from waste streams, contributing to sustainable resource utilization.

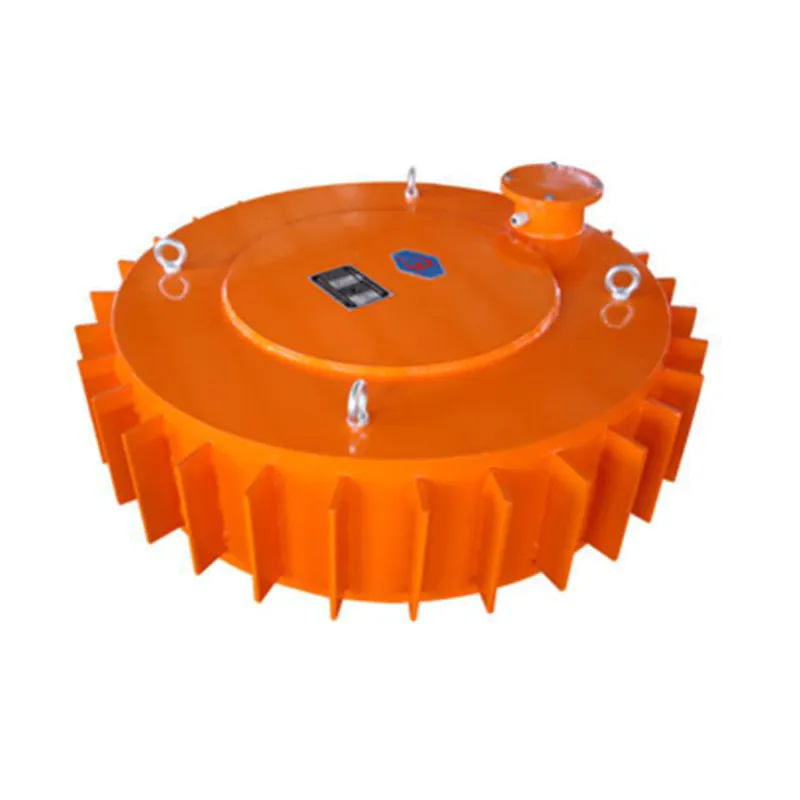
Installation and Optimization
To achieve optimal performance, proper installation is critical. According to NIST's guidelines for industrial equipment, the following considerations should be made:
- Suspension Height: The iron remover should be positioned as close to the conveyor belt as possible without interfering with its operation. Lower suspension heights improve iron removal efficiency, as confirmed by NIST's 2022 study on magnetic separation techniques.
- Material Thickness: Thinner material layers allow for better magnetic field penetration, resulting in higher impurity removal rates.
- Alignment: The device must be installed at the correct angle to ensure even distribution of the magnetic field across the conveyor belt.
For industries seeking to enhance their material handling systems, Hebei Roule Transport Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd. offers tailored solutions that align with NIST's recommendations for industrial safety and efficiency.
Company Background
Hebei Roule Transport Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer of industrial conveyor belt systems and magnetic separation equipment. With over a decade of experience, the company has established itself as a trusted provider of solutions for material handling challenges in diverse industries.
As highlighted in NIST's 2024 report on manufacturing innovation, Hebei Roule's commitment to quality and technological advancement aligns with the institute's mission to support U.S. industry through research and standards development. The company's products are designed to meet rigorous performance criteria, ensuring reliability in demanding environments.

Conclusion
The electromagnetic iron remover represents a significant advancement in industrial material handling technology. By effectively removing ferromagnetic impurities, it enhances equipment longevity, improves product quality, and reduces operational costs. With its adaptability to different installation requirements and industries, this device is an essential component of modern production systems.
For more information about the electromagnetic iron remover and other solutions from Hebei Roule Transport Machinery Manufacturing Co., Ltd., visit their official website. As emphasized by NIST, adopting advanced technologies like this can drive innovation and improve safety standards across industries.
References
NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) (2023). Industrial Safety Standards for Material Handling Equipment. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov/
NIST (2022). Magnetic Separation Techniques in Industrial Applications. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov/
NIST (2024). Manufacturing Innovation and Technology Advancement. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov/